MCUBoot¶
For different possible applications (e.g. an updated and an old one) the flash storage is split. A bootloader is used to select an specific application to start. In our case we utilize MCUBoot, which also has Zephyr utility support. The bootloader is always started at first (its partition is located at the processors start address).
Flash Partitions¶
The MCUBoot requires multiple flash partitions in the device tree. It expects specific naming conventions for these partitions:
boot_partition: required by the MCUBootslot0_partition: for primary imageslot1_partition: for secondary image
For example, take a look at the flash partitions defined in the bms.dts file. The BMS D.1 and
D.2 board has 512KB of flash memory.
&flash0 {
partitions {
...
boot_partition: partition@0 {
label = "mcuboot";
reg = <0x000000000 DT_SIZE_K(32)>;
};
slot0_partition: partition@8000 {
label = "image-0";
reg = <0x00008000 DT_SIZE_K(204)>;
};
slot1_partition: partition@3B800 {
label = "image-1";
reg = <0x0003B000 DT_SIZE_K(202)>;
};
...
};
};
The flash partitions, slot0_partition and slot1_partition, are configured to work with
swap using move algorithm. The
algorithm is enabled through the Kconfig option CONFIG_BOOT_SWAP_USING_MOVE=y (see
mcuboot.conf).
- The primary slot has additional sectors (each of 2KB) compared to the secondary slot.
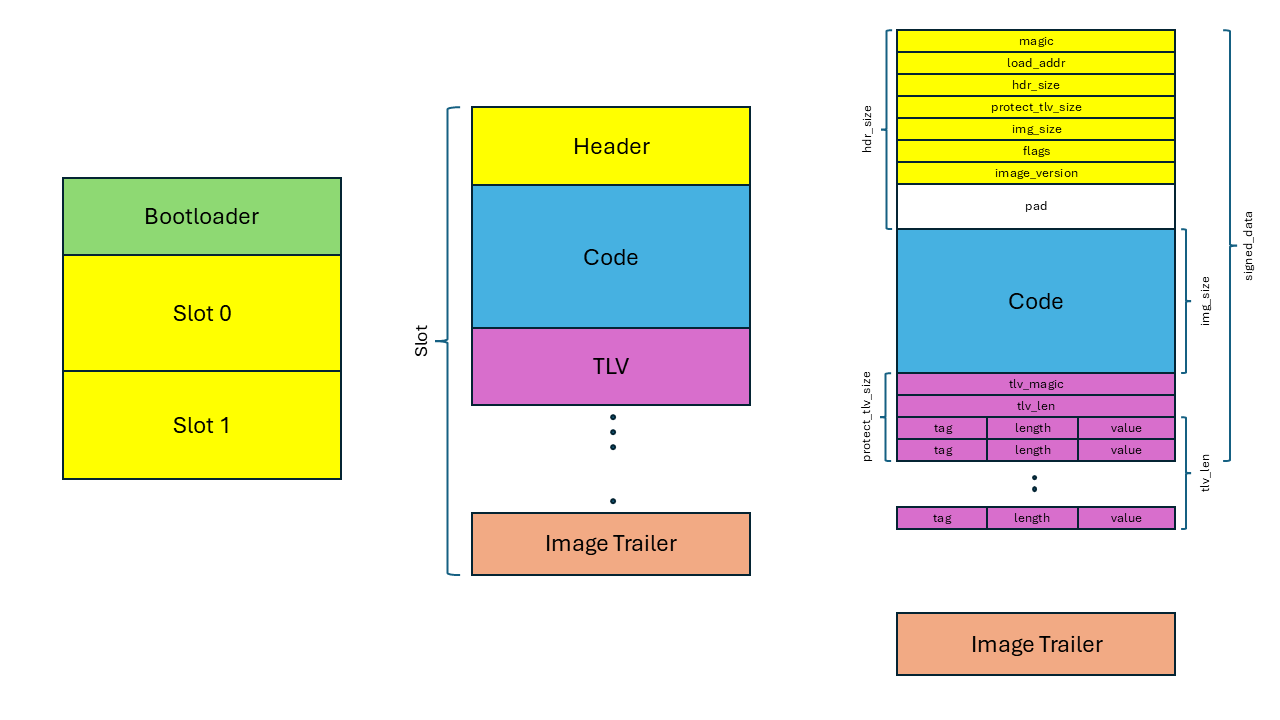
Image Format¶
When building MCUBoot compatible images, it wraps the code between a 32-byte long image header and TLV information. The MCUBoot also adds the trailer at the end of the firmware slot to store metadata about the state of the firmware image.
- The image header is a region at the beginning of a firmware image that stores essential metadata about the image such as load address, image size etc.
- TLV stores additional information, such as cryptographic signatures, image version details, and other metadata necessary for secure boot operations.
Take a look the image format in the MCUBoot design document.
MCUBoot and application with Sysbuild¶
An application automatically includes MCUboot as bootloader when built using sysbuild. This is
achieved with a sysbuild specific Kconfig configuration, sysbuild.conf. The
SB_CONFIG_BOOTLOADER_MCUBOOT=y setting in the sysbuild Kconfig file enables the bootloader when
building with sysbuild.
The sysbuild/mcuboot.conf file is used as an extra fragment that is merged together with the
default configuration files used by the MCUboot (see bootloader/mcuboot/boot/zephyr/prj.conf).
This means any MCUBoot related options can be set from this file without touching the MCUBoot repo.
Signing the application¶
The SB_CONFIG_BOOT_SIGNATURE_TYPE_NONE=y option disables the use of cryptographic signatures for
image verification instead only calculates the hash value (SHA256) of the image and stores in the
TLV section.